Boolean Searches
Elyse Kuhn and Kassandra Ruecker

Learning Objectives
Upon successful completion of this chapter, learners will be able to do the following:
-
Define key terms related to online legal research, including keywords, Boolean operators, and connectors.
-
List the advantages of online legal databases compared to print sources.
-
Identify the three main Boolean operators (AND, OR, NOT) and describe their functions.
-
Recognize different types of connectors (proximity, truncation, wildcard, substitution) and their purposes.
-
Outline the difference between plain language searches and Boolean searches.
Introduction
Legal research can be completed more efficiently online using digital sources; this is significant because it allows legal researchers to search more effectively. A large portion of the legal information is compiled into one place, meaning that the search must be specific to find the case that will most help the case. One method of searching, called a Boolean search, uses key terms to research a specific topic. This chapter will discuss why online databases are helpful. Then, it will break down different types of online searches. Later in the chapter, it will describe how Boolean searches effectively narrow the search. Finally, it will describe the different Boolean syntaxes for different online databases.
Online Searches vs. Print Searches
As a result of Canada’s common law legal system, over 150 years of case law have been compiled into online databases (Girard, 2017). When information can be found in so many different places online, it is essential to know how to search for specific information effectively. A skill necessary to succeed in the legal workplace today is knowing where to look for information and how to identify issues and narrow the search. Until the 1990s, print sources were the most common way of searching for information (Shatby, 2022). Unfortunately, print sources can be expensive, challenging to navigate, and not easily updated. For these reasons, online searches can be a more accurate, up-to-date, and efficient way to search for information. When searching online, the results are often much more specific and the surrounding context is easily accessible (Blatt & Kurtz, 2020).
Merits of Online Databases
Online databases have significantly simplified the legal research process. Online information is accessible through free sources such as CanLII. Finding tools like keyword searches and hyperlinked tables of contents helps to locate specific information quickly. The easy accessibility of information is exemplified by law books no longer having to be physically purchased. Often, online textbooks are offered at a reduced price or are available for free. Copies of this information are transportable by using hard drives or a cloud-based storage platform, making them more accessible than print sources. Many online sources are accessible from anywhere with an internet connection. Another reason online sources are helpful is that website moderators can update the information more efficiently and more frequently, resulting in a more accurate source. Online legal databases are equipped with note-up software that ensures the legislation is the most up-to-date version and that case law has not been repealed. In the same scenario, the print source cannot be updated, and a new volume of the print source would need to be published. As a result, the book would become outdated quickly, and new versions would need to be purchased often. If the old version continues to be relied on, a decision that proves a legal argument may be appealed, and now a different standard applies; this can be detrimental to a case. Commonly used online resources are listed in the drop-down menus below:
Free Resources & Government Websites
Free Resources
Government Websites
Subscription Based
Search Strategies
Research is started using keywords that come from the fact situation or legal issue presented by the client. Keywords are those that will be most effective in searching a topic. Identifying the legal issue in a fact scenario is key to finding the correct keywords. As a legal professional, general knowledge and a basic understanding of the law will aid in choosing which words will be key to the research (Blatt & Kurtz, 2020, p. 120). The Cunningham Memorial Library at Indiana State University (2024) explains the use of keywords as searching that “allows you to search for the appearance of any term, anywhere in an individual item [within] internet search engines and many online databases.” Identifying the correct keywords and phrases will improve the effectiveness of search results.
Plain or Natural Language
There are two types of keyword searches: the first is a plain or natural language search. This is a general way of performing a search online. There is no training involved, and the average person conducts these daily. For example, using Google or any other search engine is a natural language search. When little to nothing is known about a topic, this is the first step to learning more about it. Using plain/natural language to start the search helps gain a basic understanding of the topic when more information is required (Stanford Law School, 2024). An example of a plain language search would be putting the phrase legal research into Google.
Boolean Searching
Boolean searching, also known as a terms and connectors search, gives more control. It provides the database with specific information, which allows the algorithm to narrow down more relevant results. Boolean logic (named after mathematician George Boole) is a system of logic designed to yield optimal search results. The Boolean operators, AND, OR, and NOT, help construct a logical search (UOM, 2022). Combining terms and using symbols, and linking keywords and phrases with them, is what makes a Boolean search more effective when compared to a plain or natural language search.
Plain Language Search vs. Boolean Search
| BOOLEAN | PLAIN LANGUAGE |
|
More refined, narrower results; helpful for broad subjects More effective for specific subjects |
Works well when little is known about a subject Effective when needing to learn more about a subject |
Overall, just remember there is no one way to do a search, but with Boolean searches, be mindful that narrow search terms can eliminate relevant data from the results. Online databases are significant, helpful tools, and having the skilled abilities to use Boolean efficiently will take training and using different combinations of the tools presented below (DeFilippo, n.d.).
Boolean Search
Terms and Connectors
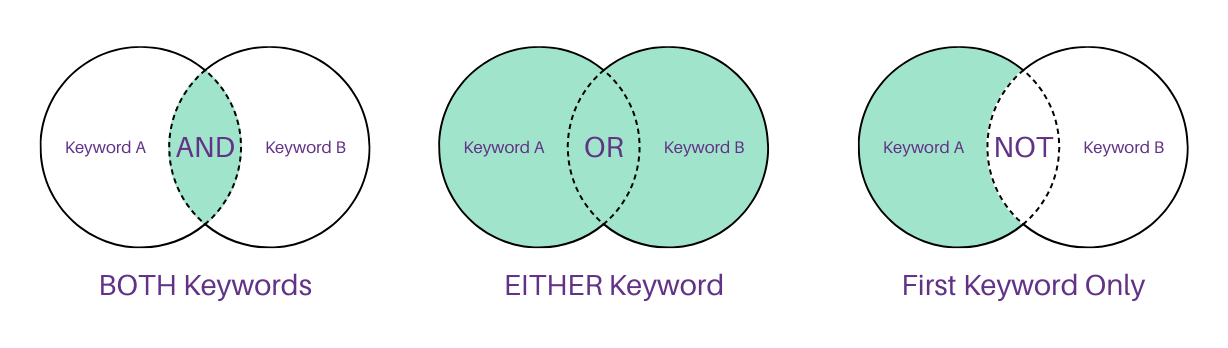
As stated above, Boolean searching is specific to an advanced version of searching online databases. Using Boolean logical operators such as AND, OR and NOT, and connectors such as proximity, truncation and substitution, helps to narrow, expand, and refine the search results in databases.
The AND connector
The AND connector links two words to inform the computer to search for their relationship, often narrowing the search results. The database will search only for documents that contain the keywords that have been connected using AND. For example, if a search is done for sources with connections to emotional support, you would search for: emotional AND support (Blatt & Kurtz, 2020, p. 125).
The OR connector
The OR connector is used to broaden search results by retrieving records that contain any of the specified terms, thereby increasing the scope of the search query. The database will search only for documents that contain any of the keywords that have been connected using OR. For example, if a search is done for cases related to business contracts, the search should cover both results with contracts or agreements and would be: contracts OR agreements.
The NOT connector
The NOT connector links two words together to inform the computer to search for documents that contain one of the keywords but not both. For example, if a search is done to find sources with information about family law but with the exclusion of sources with family violence, the search would be: family, NOT violence (Blatt & Kurtz, 2020, p. 124).
Although the Boolean search logic is the same between databases, the syntax or symbols used may vary slightly between databases. A summary comparison list of operators for Canlii, Westlaw, and LexisNexis is included at the end of this chapter.
Logical Operators Summary
Narrowing Your Search
Proximity Connectors
Proximity connectors are used in search queries to specify the closeness of keywords within a text. These connectors allow users to refine their searches by determining how closely words must appear together, which can enhance the precision of search results. By using proximity connectors, researchers can find documents where the relationship between terms is more relevant, thereby improving the accuracy and relevance of the information retrieved. Proximity connectors function like the AND operator and keyword order is only restricted with certain connectors. Different databases may treat the same connector with slightly different parameters, as outlined below.
| CONNECTOR | PROXIMITY | EXAMPLE |
| /n | Keywords are within “n” distance to each other to a maximum of 255 words. | For words within 10 words of each other, it would be landlord /10 eviction. |
| /s | Keywords are within the same sentence[1]. | cat /s purring |
| /p | Keywords are within the same paragraph[2]. | dog /p training |
| +n[3] | The first keyword must precede the second keyword within “n” words to a maximum of 255 words. | For results with landlord no greater than 10 words prior to eviction, it would be landlord +10 eviction. |
| +s[4] | The first keyword must precede the second keyword in the same sentence. | The search legal +s fees will only return results where the term legal precedes fees. |
| +p[5] | The first keyword must precede the second keyword in the same paragraph. | The search medical +s malpractice will only return results where the term medical precedes malpractice within the same paragraph. |
Searching Phrases
When searching for a specific phrase, a result will automatically be generated from that alone; this is very similar to a natural language search. For example, if a search is done for the phrase interim support, the database search will function similar to an OR search with results containing either the keyword interim or support. In order to narrow the search and receive results containing the exact phrase, place the phrase into quotation marks, “interim support.” This will generate results that only include that exact specific phrase (AustLII, n.d.).
Variant Spellings or Tenses
To accommodate the words in the English language that are spelled in different ways with similar meanings, some databases employ a substitution symbol within the word to search for all possible spellings or variations of that word. Westlaw uses an asterisk (*), also known as a wildcard symbol, to take the place of a single variable letter. Whereas, LexisNexis uses a question mark to take the place of a single variable letter. For example, entering wom*n in Westlaw or wom?n in LexisNexis in a search will find instances of both “woman” and “women,” effectively covering both singular and plural forms. Similarly, behavio*r or behavio?r can be used to retrieve results for both “behavior” and “behaviour,” accommodating differences in American and British spellings. Verb tenses can also be accommodated with this method with words such as “ran” or “run” both being results of the search r*n or r?n. However, this type of usage may also result in unintentional unrelated results such as “rin,” an outdated Japanese monetary unit. Overall, this method is particularly useful for identifying terms that share a common root but may differ in spelling, tenses, or regional usage, thereby broadening the scope of search results.
Truncation and Wildcard Searches
Many root words have multiple endings in the English language. For example, to avoid having to search for harassed, harassing, harassment, or harasses, databases allow for truncation of searches by using wildcard search operators. Unlike the substitution within words that is restricted to subscription sources, Canlii and most other free sources also use wildcard searches for the ending of words.
Example of a wildcard search:
How it works:
negligen*is the wildcard search—the asterisk (*) tells CanLII to return results for any word that starts withnegligen, such as negligent, negligence, or negligently.ANDis the Boolean operator—it ensures both terms appear in the results."standard of care"is in quotation marks to search for the exact phrase.
What it finds:
Cases that mention negligence (in any form) and also contain the exact phrase standard of care.
Using Multiple Connectors
Parentheses
Using parentheses in searching allows for more complex and precise queries by grouping terms and operators together. It allows the user to dictate the priority and order of search operations. Every database will force the contents of parentheses to be the first search condition. Similar to the use of brackets in mathematics, search term(s) or operation(s) within the parentheses will be given priority over other operators (Blatt & Kurtz, 2020, pp. 128–129). The use of parentheses within searches forms the basis of nesting.
Nesting
The use of multiple connectors will help to narrow the search, streamlining results to be very specific to the topic. Using this technique will prove to be faster when searching for specific documents. The order in which the connectors are, when using multiple, is important to keep in mind. Different databases may not read searches the same way or give the same priority to certain connectors. If the order of priority is known about the specific database being used, the search should utilize the connectors in the best way to get the results. The University of Minnesota Libraries has an excellent diagram discussing mixing Boolean operators (“nesting”).
Search Syntax for Common Legal Databases
Using Boolean searches to navigate legal databases can be difficult, especially because different databases use different connectors. This could drastically change the results of a search.
Resource Available
There are three main legal research databases that support Boolean search syntax: CanLII, Westlaw Canada, and Lexis Advance Quicklaw. Each database has its own set of Boolean operators and search rules. You can review detailed tables outlining the syntax and examples for each database through an online resource created by Elyse Kuhn, which provides side-by-side comparisons to help you construct more effective searches. These tables are available for download in MS Excel format through Google Drive.
References for Operators Table
CanLII Operators Table:
Lexum. (n.d.). Search help. https://www.canlii.org/en/info/search.html#operatorsTable
Westlaw Operators Table:
Thomson Reuters. (n.d.). Advance search: LawSource. Thomson Reuters WestLaw Canada. https://nextcanada-westlaw-com.ezproxy.macewan.ca/Search/AdvancedSearchPage.html?originUrlPath=%2FBrowse%2FHome%2FLawSource&categoryPageUrl=Home%2FLawSource&transitionType=Default&contextData=(sc.Default)&jurisdiction=CAN_LAWSOURCE&contentType=ALL
Thomson Reuters. (n.d.). Search with terms and connectors. https://www.thomsonreuters.com/en-us/help/westlaw-edge/searching/search-with-terms-and-connectors.html
Thomson Reuters. (2019). How to search with Boolean terms and connectors. Thomson Reuters WestLaw. https://support.thomsonreuters.com.au/sites/default/files/2020-10/Westlaw%20Classic%20-%20Boolean%20Terms%20and%20Connectors.pdf
LexisNexis Operators Table:
LexisNexis. (n.d.). Connector order and priority. Nexis Uni help. https://help.lexisnexis.com/Flare/nexisuni/US/en_US/Content/reference/connectorpriority_ref.htm
LexisNexis. (n.d.). Proximity connectors. Nexis Uni help. https://help.lexisnexis.com/Flare/nexisuni/US/en_US/Content/reference/connectorsproximity_ref.htm
LexisNexis. (n.d.). Search connector wildcards. Nexis Uni help. https://help.lexisnexis.com/Flare/nexisuni/US/en_US/Content/reference/connectorswildcard_ref.htm
LexisNexis. (n.d.). Searching for symbols or other special characters. Nexis Uni help. https://help.lexisnexis.com/Flare/nexisuni/US/en_US/Content/reference/listofspecialchars_ref.htm
LexisNexis. (n.d.). Search term connectors. Nexis Uni help. https://help.lexisnexis.com/Flare/nexisuni/US/en_US/Content/reference/connectors_ref.htm
LexisNexis. (n.d.). Using NOT with proximity connectors. Nexis Uni help. https://help.lexisnexis.com/Flare/nexisuni/US/en_US/Content/reference/notproximity_ref.htm
LexisNexis. (n.d.). Using quotation marks to find exact matches. Nexis Uni help. https://help.lexisnexis.com/Flare/nexisuni/US/en_US/Content/reference/usequotes_ref.htm
Building a Boolean Search
The first thing to do when conducting any search is to determine which keywords to use from the information given or the legal issue presented. Let’s run with the following example:
Your client was hit by a car in a pedestrian crosswalk, and you have been given the task of researching the issue. The client is suing the driver because they have lost income due to the inability to work because of the accident. They feel the driver was careless and negligent for failing to notice them in the crosswalk. They would like some compensation for their pain and suffering.
- Determine keywords: careless, driving, negligence, pain, suffering, income, and loss
- Determine if any of the keywords can be used in a phrase or put together as a concept. Here we could combine careless driving and income loss.
- Use any synonyms of the keywords and connect them with OR. Negligence OR carelessness.
- Decide if any of the keywords can be substituted or truncated. In this case, truncate drive! and suffer!.
- Take the keywords and alternatives and combine them using Boolean connectors and proximity connectors.
The following is the final result of steps 1–5 as explained above:
Damages/10 negligence OR careless! AND pain OR suffer! AND "“loss of income“
The quotations around pain and suffering, and loss of income, to search for results with those exact phrases. Remember to use parentheses to force the priority of any one thing within your search (Blatt & Kurtz, 2020, p. 130).
Structuring Your Boolean Search
|
Step One: Brainstorm |
|
Photocopies, classroom, and copyright infringement look like the key terms in this prompt. |
|
Step Two: Synonyms, Root Expanders, and Quotation Marks |
|
Photocopy is pretty specific—a court might also discuss reproductions more broadly. Since either of these terms would be useful, consider linking them together with an “OR” connector and group them with parentheses: (photocopy OR reproduction). Similarly, with the classroom, let’s try education too: (classroom OR education). |
|
What if the court writes about reproducing material but not reproduction? Or educational material, not education? Putting an exclamation point (!) at the end of a string can ensure results for all possible endings. Let’s do that with all our terms where it makes sense: (photocop! OR reproduc!) (class! OR educat!). (We will evaluate copyright infringement next.) |
|
Quotation marks will search for a series of words as a phrase—those exact words—in that order. We are interested in “copyright infringement,” not copyright by itself or infringement by itself. |
|
Now our search string is: (photocop! OR reproduc!) (class! OR educat!) “copyright infringement” |
|
Step Three: Connect Your Terms |
|
The AND connector requires everything linked by the AND to appear in the search results. These can be individual terms, groups of synonyms linked by OR, groups with parentheses, or entire complex search strings. We need all of these term groups and phrases to be in our search results: (photocop! OR reproduc!) AND (class! OR educat!) AND “copyright infringement” |
|
However, we are only interested in photocopies made for classroom use, which means those specific terms must be near each other in any relevant case. To ensure those terms both appear in the search results, and are used near each other, use a proximity operator: /p, /s, or /n (replacing n with a number representing the number of words between the terms). Try /s, meaning that the terms have to appear in the same sentence; we can broaden that to /p (paragraph) if needed. The final result is: (photocop! OR reproduc!) /s (class! OR educat!) AND “copyright infringement” |
Summary
Learning how to successfully demonstrate effective legal research is key to being a great paralegal; your research abilities will make you a great asset for lawyers, as you make their preparation easier. When using online legal databases, knowing how to utilize Boolean searches can give the user significant control over the results. Without this control, you will end up with too many results, and sifting through them all is much less efficient. Keep in mind that the connectors within each legal database vary, but once the basics are known, you will be able to work the system to deliver the best results. These will vary based on each situation, but what is wanted every time is results that deliver the most useful information, specific to the situation, in the smallest quantity.
Practical Application
You are researching cases where a handwritten will was challenged because it was missing key elements or was deemed invalid. The case involves a dispute between siblings over the distribution of farmland.
-
Determine the key legal concepts and potential synonyms to organize search terms, depending on the online database available to you.
-
Develop a Boolean search that finds Alberta cases discussing holograph wills and disputes over agricultural property.
-
Use a combination of AND, OR, proximity operators, and a wildcard to broaden your search where appropriate.
Note your answers. When you are ready, click below to reveal the sample answer.
Sample Answer
Model Boolean Search (CanLII example):
- “holograph will” OR “handwritten will” AND disput* AND (farm* OR agricultur*) AND Alberta
Why this works:
- “holograph will” OR “handwritten will” – This captures both the formal legal term and its plain-language equivalent.
- disput* – Truncation captures dispute, disputed, disputing, disputes.
- (farm OR agricultur)** – Truncation and OR capture farmland, farmer, farming, agriculture, agricultural.
- Alberta – Restricts results to Alberta-specific content (also possible via database jurisdiction filter).
More Complex Version with Proximity (Westlaw Canada example):
- (“holograph will” OR “handwritten will”) AND disput* /p (farm* OR agricultur*)
Why this works:
- /p – This ensures dispute-related terms appear in the same paragraph as farming or agricultural terms, thus increasing relevance.
- This reduces results about unrelated disputes and focuses on estate disputes involving agricultural property.
Reflection Questions
-
Think about a recent research task you completed. How could using Boolean operators have improved the precision and relevance of your search results?
-
When working in multiple legal databases (e.g., CanLII, Westlaw, Lexis Advance Quicklaw), how will you ensure you are using the correct syntax for each to avoid missing key results?
-
Describe a scenario where using too many restrictive Boolean operators could harm the quality of your search. How would you adjust your search strategy in that case?
-
How could proximity connectors help you find more relevant case law when researching a complex legal issue for your supervising lawyer?
-
Why is it important for legal assistants and paralegals to understand wildcard and truncation searches, and how could you apply these tools to handle variations in spelling, tense, or terminology in your research?
References
AustLII. (n.d.). Help: Boolean operators chart. AustLII. https://www.austlii.edu.au/worldlii/help/boolean.html
Blatt, A., Kerr, M. H., & Kurtz, J. (2020). Legal research: Step by step (5th ed.). Emond Montgomery Publications.
DeFilippo, T. (n.d.). Refining searches using Boolean operators. University [of Nevada] Writing & Speaking Center. https://www.unr.edu/writing-speaking-center/writing-speaking-resources/boolean-operators
Girard, P. (2017, February 20). That’s history: The roots of common law in Canada. Law Times. https://www.lawtimesnews.com/archive/thats-history-the-roots-of-common-law-in-canada/262430
Indiana State University. (2024, April 2). Library basics: Keyword/Boolean searching (K/B): An introduction. https://library.indianastate.edu/librarybasics/keywords
LexisNexis. (n.d.a). Connector order and priority. Nexis Uni help. https://help.lexisnexis.com/Flare/nexisuni/US/en_US/Content/reference/connectorpriority_ref.htm
LexisNexis. (n.d.b). Proximity connectors. Nexis Uni help. https://help.lexisnexis.com/Flare/nexisuni/US/en_US/Content/reference/connectorsproximity_ref.htm
LexisNexis. (n.d.c). Search connector wildcards. Nexis Uni help. https://help.lexisnexis.com/Flare/nexisuni/US/en_US/Content/reference/connectorswildcard_ref.htm
LexisNexis. (n.d.d). Searching for symbols or other special characters. Nexis Uni help. https://help.lexisnexis.com/Flare/nexisuni/US/en_US/Content/reference/listofspecialchars_ref.htm
LexisNexis. (n.d.e). Search term connectors. Nexis Uni help. https://help.lexisnexis.com/Flare/nexisuni/US/en_US/Content/reference/connectors_ref.htm
LexisNexis. (n.d.f). Using NOT with proximity connectors. Nexis Uni help. https://help.lexisnexis.com/Flare/nexisuni/US/en_US/Content/reference/notproximity_ref.htm
LexisNexis. (n.d.g). Using quotation marks to find exact matches. Nexis Uni help. https://help.lexisnexis.com/Flare/nexisuni/US/en_US/Content/reference/usequotes_ref.htm
Lexum. (n.d.). Search. CanLII. https://www.canlii.org/en/info/search.html#operatorsTable
Michigan State University. (2023, October 4). Boolean searching in legal databases: /N, /S, /P. LibGuides at Michigan State University College of Law. https://law-msu.libguides.com/c.php?g=913167&p=6580326
Regents of the University of Minnesota. (2022, June 30). Boolean operators: A cheat sheet. Library Research Guides. https://libguides.umn.edu/BooleanOperators
Shatby, S. E. (2022, June 1). The history of data: From ancient times to modern day. 365 Data Science. https://365datascience.com/trending/history-of-data/#7
Stanford Law School. (2024, February 28). LibGuides: Case finding and advanced searching strategies. LibGuides at Stanford Law School. https://guides.law.stanford.edu/cases/boolean
Thomson Reuters. (n.d.a). Advance search: LawSource. Thomson Reuters WestLaw Canada. https://nextcanada-westlaw-com.ezproxy.macewan.ca/Search/AdvancedSearchPage.html?originUrlPath=%2FBrowse%2FHome%2FLawSource&categoryPageUrl=Home%2FLawSource&transitionType=Default&contextData=(sc.Default)&jurisdiction=CAN_LAWSOURCE&contentType=ALL
Thomson Reuters. (n.d.b). Choose Boolean connectors. https://www.thomsonreuters.com/en-us/help/westlaw-edge/searching/choose-connectors.html
Thomson Reuters. (n.d.c). Operators table. Thomson Reuters WestLaw Canada. https://nextcanada.westlaw.com/Search/AdvancedSearchPage.html?originUrlPath=%2FBrowse%2FHome%2FLawSource&categoryPageUrl=Home%2FLawSource&transitionType=Default&contextData=(sc.Default)&jurisdiction=CAN_LAWSOURCE&contentType=ALL
Thomson Reuters. (n.d.d). Search with terms and connectors. https://www.thomsonreuters.com/en-us/help/westlaw-edge/searching/search-with-terms-and-connectors.html
Thomson Reuters. (2019). How to search with Boolean terms and connectors. Thomson Reuters WestLaw. https://support.thomsonreuters.com.au/sites/default/files/2020-10/Westlaw%20Classic%20-%20Boolean%20Terms%20and%20Connectors.pdf
Trellis. (2023). Using Boolean operators in smart search. Trellis Research Knowledge Base. https://support.trellis.law/boolean-operators
- Within LexisNexis, the /s operator actually searches within 25 words and is not restricted to the exact sentence.. ↵
- With LexisNexis, this will search within 75 words as each other, not necessarily within the same paragraph. ↵
- Not available in Canlii. ↵
- Not available in Canlii. ↵
- Not available in Canlii. ↵
A keyword is a specific word or phrase used in a search query to retrieve relevant information or content. Keywords are essential in indexing and finding data in databases, search engines, and information systems, serving as the primary terms that describe the subject or focus of the search.
A type of search where a user inputs language into the search field in a manner that reflects natural speech or writing.
A type of search that employs keywords alongside search syntax such as AND, OR, and NOT, which define the relationship between keywords to help the computer identify relevant results.
A nesting search, in research search queries, is a technique that uses parentheses to group related keywords and logical operators, such as AND, OR, and NOT, to structure the search logic.

